
Mary Walker
Mary Broadfoot Walker (1888 - 1974) was a Scottish physician. Mary Walker effect (1934); neostigmine and myasthenia gravis

Mary Broadfoot Walker (1888 - 1974) was a Scottish physician. Mary Walker effect (1934); neostigmine and myasthenia gravis

Frederic Jay Cotton (1869–1939) was an American Orthopedic Surgeon. Eponymously affiliated with the Cotton fracture (trimalleolar fracture) and Cotton-Loader position (hyper-flexed wrist with ulna deviation in closed reduction of distal radius fractures)

Albert Hoffa (1859-1907) was a German orthopedic surgeon. eponymously affiliated with a distal femur fracture (1888); an operation for congenital hip dislocations (1890); the development of a system of massage therapy, the Hoffa system (1893); and the Hoffa fat pad

Bernhard Georg (Hardy) Weber (1927 – 2002) was a Swiss surgeon affiliated with the Danis-Weber ankle fracture classification. Medical Eponym

Shoulder Dislocations. Adult Orthopedic case interpretation. A review of Xray and ultrasound (POCUS) evaluation, dislocation types and reduction techniques
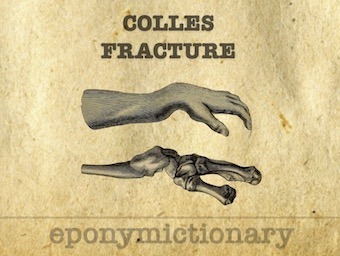
Colles fracture: Extra-articular fracture of the distal radius with dorsal angulation of the distal fragment. Abraham Colles (1814)

Abraham Colles (1773 - 1843) was an Irish surgeon and anatomist. Eponym: Colles Fracture (1814) distal radius/ulna fracture
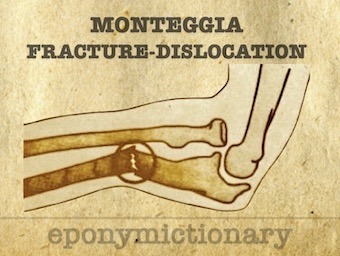
Monteggia fracture. Fracture of the proximal or middle third of the ulna with associated radial head dislocation/instability. GB Monteggia 1812

José Luis Bado (1903 – 1977) was a Uruguayan surgeon. Eponymously linked to the Bado classification of Monteggia fractures.

Riccardo Galeazzi (1866-1952) was a pioneering Italian orthopaedic surgeon. The eponymous Galeazzi fracture is named after him.

Giovanni Battista Montéggia (1762-1815) was an Italian surgeon. Eponym: Monteggia fracture (1812) ulna fracture, radial head dislocation

Galeazzi fracture (1934). Fracture of the distal third of the radius with associated Distal radio-ulna joint (DRUJ) disruption.